Overview
Glimepiride is a sulfonylurea blood-sugar-lowering agent. It stimulates insulin release from pancreatic beta cells. This release mainly relies on improved responsiveness of these cells to physiological glucose stimulus. Glimepiride increases the normal action of insulin on peripheral glucose uptake. It also mimics such action as well as the glucose output of the liver. A single dose of ATMOGLIM can ensure good metabolic control over 24 hours.
WHAT IS ATMOGLIM AND WHAT IT IS USED FOR?
ATMOGLIM contains the active substance glimepiride. Glimepiride belongs to a group of medicines called oral hypoglycaemics. These medicines help to lower your blood sugar (glucose) if you suffer from Type 2 diabetes (diabetes mellitus). Your doctor will prescribe Glimepiride for you if your diabetes cannot be controlled just by good diet, regular exercise or weight loss.
What ATMOGLIM is used for?
ATMOGLIM is used to treat a certain form of diabetes (type 2 diabetes mellitus) when diet, physical exercise and weight reduction alone have not been able to control your blood sugar levels.
Why is this medication prescribed?
Glimepiride, the active ingredient of ATMOGLIM, is a blood-sugar-lowering agent belonging to the sulfonylurea group. The decrease in blood sugar is achieved principally by means of the stimulation of insulin release from pancreatic beta cells. This effect is predominantly based on improved responsiveness of these cells to the physiological glucose stimulus. Glimepiride augments the normal action of insulin on peripheral glucose uptake. Moreover, it mimics such action as well as the glucose output of the liver. Good metabolic control over 24 hours can be achieved with a single dose of ATMOGLIM.
Warnings
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking your medicine if:
You are recovering from an injury, operation, infections with fever, or from other forms of stress, inform your doctor as temporary change of treatment may be necessary.
Lowering of the haemoglobin level and breakdown of red blood cells (haemolytic anemia) can occur in patients missing the enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase.
The information available on the use of ATMOGLIM in people under 18 years of age is limited. Therefore, its use in these patients is not recommended.
Contraindications
Do not take Glimepiride and tell your doctor if:
You are allergic to: glimepiride or other sulfonylureas (medicines used to lower your blood sugar such as glibenclamide) or sulfonamides (medicines for bacterial infections such as sulfamethoxazole) or any of the other ingredients of this medicine.
You have insulin dependent diabetes (type 1 diabetes mellitus).
You have diabetic ketoacidosis (a complication of diabetes when your acid level is raised in your body and you may have some of the following signs: fatigue, feeling sick (nausea), frequent urination and muscular stiffness).
You are in a diabetic coma.
You have severe kidney disease.
You have a severe liver disease.
Do not take this medicine if any of the above apply to you. If you are not sure, talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking Glimepiride.Pregnancy and breast-feeding: ATMOGLIM should not be taken during pregnancy. Tell your doctor if you are, you think you might be or are planning to become pregnant.
Breast-Feeding: ATMOGLIM may pass into breast milk. ATMOGLIM should not be taken during breast-feeding.
Side Effects
Dizziness, headache, tired feeling
Mild nausea, vomiting, stomach pain, diarrhea
Increased skin sensitivity to sunlight
Mild itching or skin rash
Pale skin, easy bruising or bleeding, fever, unusual weakness
Severe skin rash, itching, redness, or irritation
Numbness or tingly feeling
Trouble breathing
Dark urine, clay-colored stools
Upper stomach pain, low fever, jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes)
Dosage
This is Prefered Dosage:
The dose depends on your needs, condition and results of blood and urine sugar tests and is determined by your doctor. Do not take more tablets than your doctor has prescribed.
The usual starting dose is one 1mg tablet once a day. If necessary, your doctor may increase the dose after each 1 - 2 weeks of treatment. The maximum recommended dose is 6mg Amaryl per day. Your dose of ATMOGLIM may need to be adjusted if you change weight, change your lifestyle, or if you are under a lot of stress. Please speak to your doctor if any of these situations apply to you. If you feel the effect of your medicine is too weak or too strong do not change the dose yourself, but ask your doctor.
Disclaimer:To be taken only after consulting with the doctor.
Storage
Keep out of the reach and sight of children. Do not use after the expiry date which is stated after 'EXP' on the blister and carton. The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
ATMOGLIM 1 mg, 2 mg, 3 mg, and 4 mg tablets: Do not store above 30°C. Store in the original package. Do not use if you notice visible signs of deterioration. Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. These measures will help to protect the environment.
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Glimepiride is a sulphonylurea antihyperglycemic agent that may be given in a single daily dose. It acts by stimulating insulin release from pancreatic beta-cells and possibly also via extrapancreatic mechanisms. The major site of activity of Glimepiride is thought to be membrane receptors on pancreatic beta-cells, where it acts via ATP-regulated potassium (KATP) channels, resulting in membrane depolarisation and release of insulin. Glimepiride is also internalised into pancreatic beta-cells, where it associates with secretory granules. This internalisation is thought to reflect insulinotropic mechanisms of Glimepiride other than at potassium channels. Glimepiride decreases blood glucose and increases blood insulin levels, with maximum effects during the first 4 hours after the dose.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption:
Bioavailability is 100%. Cmax is about 103 to 591 ng/mL (dose dependent). T max is about 2 to 3 h.
Food:
Tmax increased, and C max and AUC are slightly decreased.
Distribution:
Vd is 8.8 L. Protein binding is more than 99.5%.
Metabolism:
Completely metabolized by oxidation via CYP-450 2C9. Major metabolites are cyclohexylhydroxymethyl (M1) (about one-third of the activity of the parent) and carboxyl (M2) derivatives.
Elimination:
About 60% is excreted in urine and about 40% in feces as metabolites. The half-life is about 5 to 9.2 h.
Peak:
2 to 3 h.
Duration:
24 h.
Special Populations
Renal Function Impairment:
Serum levels decrease, M1 and M2 levels increase, and half-lives for M1 and M2 increase.
Elderly:
Mean AUC was about 13% lower. Mean weight-adjusted Cl was about 11% higher.
Children:
Mean AUC, Cmax, and half-life are comparable with adults.
Gender:
No differences in pharmacokinetics when adjustment was made for differences in body weight.
Race:
Does not appear to affect the pharmacokinetics.
INTERACTIONS
The hypoglycemic action of sulfonylureas may be potentiated by certain drugs, including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and other drugs that are highly protein bound, such as salicylates, sulfonamides, monoamine oxidase inhibitors, and beta adrenergic blocking agents. Certain drugs tend to produce hyperglycemia and may lead to loss of control. These drugs include the thiazides and other diuretics, corticosteroids, phenothiazines, thyroid products, estrogens, oral contraceptives, phenytoin, nicotinic acid, sympathomimetics, and isoniazid. Coadministration of aspirin and Glimepiride led to a 34% decrease in the mean Glimepiride AUC and, therefore, a 34% increase in the mean CL/f. The mean Cmax had a decrease of 4%. Blood glucose and serum C-peptide concentrations were unaffected and no hypoglycemic symptoms were reported.
For Patients
Information for Patients:
Azithromycin Tablets can be taken with or without food. Patients should also be cautioned not to take aluminum- and magnesium-containing antacids and azithromycin simultaneously.
•Do not use this medication if you are allergic to glimepiride, or if you are in a state of diabetic ketoacidosis (call your doctor for treatment with insulin).
• Before taking glimepiride, tell your doctor if you are allergic to sulfa drugs, or if you have heart disease, liver disease, kidney disease, an enzyme deficiency (G6PD), adrenal or pituitary gland problems, or if you are under-nourished.
•Take care not to let your blood sugar get too low. Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) can occur if you skip a meal, exercise too long, drink alcohol, or are under stress. Symptoms include headache, hunger, weakness, sweating, tremor, irritability, or trouble concentrating. Carry hard candy or glucose tablets with you in case you have low blood sugar. Other sugar sources include orange juice and milk. Be sure your family and close friends know how to help you in an emergency.
•Glimepiride is only part of a complete program of treatment that also includes diet, exercise, and weight control. Follow your diet, medication, and exercise routines very closely. Changing any of these factors can affect your blood sugar levels.
Chemistry
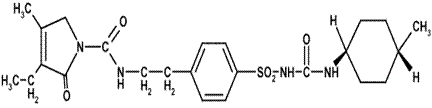
Glimepiride is an oral sulfonylurea that contains the active ingredient glimepiride. Chemically, Glimepiride is identified as 1-[[p-[2-(3-ethyl-4-methyl-2-oxo-3-pyrroline-1carboxamido) ethyl]phenyl]sulfonyl]-3-(trans-4-methylcyclohexyl)urea (C24H34N4O5S) with a molecular weight of 490.62. Glimepiride is a white to yellowish-white, crystalline, odorless to practically odorless powder and is practically insoluble in water.
Clinical Data
Pregnancy category | US: C |
Legal status | Rx-only |
Routes | Oral |